This article may contain affiliate links. Please see our affiliate disclaimer in the footer menu for more information. Thank you for your support!
Adverbs are well-known for modifying (describing) verbs, but can adverbs modify adjectives too? As a proofreader who has studied the parts of speech extensively, I can help you answer this question.
Adverbs can modify adjectives. They typically answer the question to what extent or how about the adjectives they modify. An adverb should always be placed immediately before the adjective it describes. Adverbs can also modify verbs and other adverbs.
Let’s ensure we have a tight grip on adverbs and adjectives as parts of speech. Once our knuckles are white 😉, we’ll explore numerous examples of adverbs modifying adjectives. Then, you’ll get the chance to take a quiz to check your understanding.
What Are Adverbs?
Adverbs are one of the eight parts of speech in the English language.
Here are the parts of speech:
- nouns
- pronouns
- verbs
- adjectives
- adverbs
- prepositions
- conjunctions
- interjections
Let’s see an excellent definition for the word adverb:
“Adverbs are words that usually modify—that is, they limit or restrict the meaning of—verbs. They may also modify adjectives, other adverbs, phrases, or even entire sentences.”
– Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary
When adverbs modify (i.e., describe) a verb, adjective, or other adverb, they generally answer one of the following questions:
- How?
- When?
- Where?
- To what extent? (How often? or How much?)
Let’s see some examples of adverbs in action!
An Adverb Modifying a Verb
Example: The tree swayed gently in the breeze.
The adverb gently modifies the verb swayed.
Explanation: Gently describes how the tree swayed.
- How did the tree sway? (gently)
An Adverb Modifying an Adjective
Example: The girl was particularly interested in watching the seagulls.
The adverb particularly modifies the adjective interested.
Explanation: Particularly describes to what extent (how much) the girl was interested in watching the seagulls.
- To what extent was she interested? (particularly)
Of course, we’ll see more examples like this soon! 😊
An Adverb Modifying an Adverb
Example: Sara plays the piano quite well.
The adverb quite modifies the adverb well.
Explanation: Quite tells us how well Sara plays the piano.
- How well does she play? (quite)
Now that we’re clear on adverbs, let’s make sure we have a good grasp on adjectives!
What Are Adjectives?
Like adverbs, adjectives are one of the parts of speech in English.
Let’s see a solid definition for the word adjective:
“Adjectives describe or modify—that is, they limit or restrict the meaning of—nouns and pronouns. They may name qualities of all kinds: huge, red, angry, tremendous, unique, rare, etc.”
– Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary
When adjectives modify a noun or pronoun, they ordinarily answer one of the following questions:
- What kind?
- Which one?
- How many?
Let’s see some examples of adjectives in action!
An Adjective Modifying a Noun
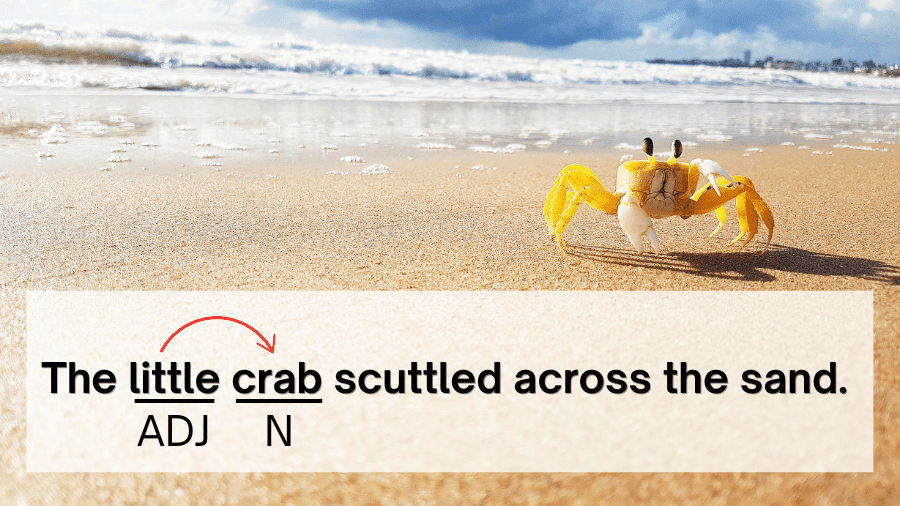
Example: The little crab scuttled across the sand.
The adjective little modifies the noun crab.
Explanation: Little tells us which crab (which one) scuttled across the sand.
- Which crab scuttled? (the little one)
An Adjective Modifying a Pronoun
Example: The puppy was cute. It was affectionate too.
The adjective affectionate modifies the pronoun it.
(It is a pronoun that’s replacing the noun puppy.)
Explanation: Affectionate tells us what kind of puppy it is.
- What kind of puppy is it? (an affectionate one)
Now that we understand adverbs and adjectives, let’s focus on sentences with adverbs modifying adjectives.
Adverbs Can Modify Adjectives
As we’ve learned, adverbs can modify adjectives.
Before we see several examples, here’s a table showing the main differences between these two parts of speech.
Adverbs vs. Adjectives
| Adverbs | Adjectives | |
|---|---|---|
| Parts of Speech They Modify | verbs, adjectives, & adverbs | nouns & pronouns |
| Questions They Answer | How? When? Where? To what extent? (How often? or How much?) | What kind? Which one? How many? |
When adverbs modify adjectives, they usually answer the question to what extent? or how? about the adjectives they describe.
You’ll see from the examples below that an adverb always precedes the adjective it modifies.
Rule: Adverbs that modify adjectives come right before the word they modify.
You’ll also observe how adverbs make our writing clearer and more nuanced when they describe adjectives. They add an appealing layer of subtlety to our communication.
However, it’s important to remember that while adverbs can help clarify our message, we shouldn’t overuse them.
Overusing adverbs can turn that layer of subtlety that makes our writing dynamic into a dull coating that takes the sparkle out of our sentences.
If you can come up with a more descriptive or colorful verb or adjective to use in place of an adverb, do it! 😊
Let’s see two examples.
Good: Patrick plays the oboe really well.
Let’s punch up our prose with this version:
Better: Patrick plays the oboe brilliantly.
And one more:
Good: Luisa ran very fast to catch the bus.
Better: Luisa raced to catch the bus.
Top-Notch Tip: If you can’t think of a better adverb to replace your verb or adjective, consult a thesaurus. I use the Merriam-Webster.com Thesaurus.

Examples of Adverbs Modifying Adjectives

Onward to the examples!
1) Example: The river looks particularly inviting.
The adjective in this sentence is inviting.
Inviting modifies (describes) the noun river. (river = inviting)
Explanation: The adverb particularly tells us how inviting the river looks.
- How inviting does the river look? (particularly)
2) Example: He was thoroughly prepared to take the test.
The adjective in this sentence is prepared.
Prepared modifies the pronoun he. (he = prepared)
Explanation: The adverb thoroughly lets us know how prepared he was.
- How prepared was he? (thoroughly)
3) Example: Tarak seemed perfectly happy to be alone.
The adjective in this sentence is happy.
Happy modifies the noun Tarak. (Tarak = happy)
Explanation: The adverb perfectly tells us how happy Tarak seemed to be alone.
- How happy did Tarak seem? (perfectly)
4) Example: The author of this article is certifiably crazy. 😉
The adjective in this sentence is crazy.
Crazy modifies the noun author. (author = crazy)
Explanation: The adverb certifiably tells us how crazy the author is.
- How crazy is the author? (certifiably)
5) Example: The puppy seems fairly calm now that the storm is over.
The adjective in this sentence is calm.
Calm modifies the noun puppy. (puppy = calm)
Explanation: The adverb fairly tells us how calm the puppy seems.
- How calm does the puppy seem? (fairly)
Before you try the quiz, let’s see the answers to some commonly asked questions.
Frequently Asked Questions

What cannot be modified by adverbs?
In terms of parts of speech, adverbs cannot modify nouns, pronouns, or interjections. They can, however, modify verbs, adjectives, and adverbs. They can even modify prepositions and conjunctions in rare instances. Finally, adverbs can modify a word, a phrase, and even an entire sentence.
I wrote an article called “What Do Adverbs Modify? (+ Examples and a Quiz)” if you’d like to learn more about this topic.
How do adjectives differ from adverbs of manner?
Adjectives are a part of speech that modify (i.e., describe) nouns and pronouns. They normally tell us what kind, which one, or how many about the word they describe. Adverbs of manner are a type of adverb that modifies verbs and adjectives. They tell us how an action is performed.
Can an adjective modify an adjective?
Adjectives cannot modify adjectives; they can only modify nouns and pronouns. The part of speech that can modify an adjective is an adverb. In addition to modifying adjectives, adverbs also modify verbs and other adverbs.
Quiz: Adverbs Modifying Adjectives
Welcome to the quiz!
If you get a question wrong, I’ll show you the correct answer and give you an explanation.
And if you’d like to continue learning about adverbs, Om Proofreading has a post about whether adverbs are able to modify other adverbs.
Have fun! 😊
Important: After completing the quiz, please scroll back up the page and click the “View score” button.
I hope this article has answered your question about whether adverbs can modify adjectives.
Best wishes to you!
“Believe in yourself and all that you are. Know that there is something inside you that is greater than any obstacle.”
– Christian D. Larson

Recent Posts
Punctuation is important because it enables us to communicate our message clearly and effectively. Without punctuation, we wouldn’t understand how units of a sentence relate to one another or how...
Although you're probably somewhat familiar with adverbs, you may be unaware of sentence adverbs. As a trained proofreader who has studied the parts of speech, I can help you understand this unique...
